The overhead lines conductors Pin type insulator should be supported on the poles or towers in such a way that currents from conductors do not flow to earth through supports. The insulators provide necessary insulation between line conductors and supports and thus prevent any leakage current from conductors to earth.
Properties of Good Insulators-
❑High mechanical strength in order to withstand conductor load , wind load etc.
❑Very high electrical resistance of insulator material in order to avoid leakage current to earth.
❑High relative permittivity of insulator material so that dielectric strength is high.
❑Non-porosity of insulator materials, free from impurities and cracks otherwise the permittivity will be lower.
❑ Unaffected from temperature variation.
❑High ratio of puncture strength to flashover voltage.
Type of Insulators Used in Transmission lines–
There are 5 types of insulators used in transmission lines as overhead insulation:
1-Pin Insulator
2- Suspension Insulator
3- Strain Insulator
4-Stay Insulator
5- Shackle Insulator
Pin, Suspension, and Strain insulators are used in medium to high voltage systems. While Stay and Shackle Insulators are mainly used in low voltage applications
Pin type insulator-
Pin insulators are the earliest developed overhead insulator, but are still commonly used in power networks up to 33 kV system. Pin type insulator can be one part, two parts or three parts type, depending upon application voltage. In a 11 kV system we generally use one part type insulator where whole pin insulator is one piece of properly shaped porcelain or glass.
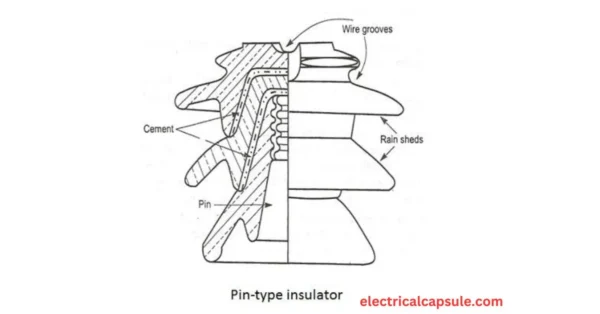
As the leakage path of insulator is through its surface, it is desirable to increase the vertical length of the insulator surface area for lengthening leakage path. We provide one, two or more rain sheds or petticoats on the insulator body to obtain long leakage path.
In addition to that rain shed or petticoats on an insulator serve another purpose. We design these rain sheds or petticoats in such a way that while raining the outer surface of the rain shed becomes wet but the inner surface remains dry and non-conductive. So there will be discontinuations of conducting path through the damp pin insulator surface.
In higher voltage systems – like 33KV and 66KV – manufacturing of one part porcelain pin insulator becomes more difficult. The higher the voltage, the thicker the insulator must be to provide sufficient insulation. A very thick single piece porcelain insulator is not practical to manufacture.
In this case, we use multiple part pin insulator, where some properly designed porcelain shells are fixed together by Portland cement to form one complete insulator unit. We generally use two parts pin insulators for 33KV, and three parts pin insulator for 66KV systems.
Exam point Pin type insulator–
1-A Pin insulator is made of non- conducting materials such as glass, porcelain , polymer and plastic.
2- The pin type insulator from its lower end is screwed to the cross-arm of a pole .
3-There is a groove on the upper end of the insulator for housing the conductor.
4-The conductor passes through this groove and it is bound by the annealed wire of the same material as the conductors.
5-Insulator surface is glazed preferably from dark brown colour polish to prevent it from moisture, dust and atmospheric gases effect.
6-Pin insulator are used for distribution of electric power at voltage up to 33KV.
7-Beyond operating voltage of 33 KV , the pin type insulators become too bulky and uneconomical.
Designing Consideration of Electrical Pin Insulator-
The live conductor attached to the top of the pin insulator which is at the live potential. We fix the bottom of the insulator to supporting structure of earth potential. The insulator has to withstand the potential stresses between conductor and earth. The shortest distance between conductor and earth, surrounding the insulator body, along which electrical discharge may take place through the air, is known as flashover distance.
When the insulator is wet, its outer surface becomes almost conducting. Hence the flashover distance of insulator is decreased. The design of an electrical insulator should be such that the decrease of flashover distance is minimum when the insulator is wet. That is why the uppermost petticoat of a pin insulator has umbrella type designed so that it can protect, the rest lower part of the insulator from the rain. The upper surface of the topmost petticoat is inclined as less as possible to maintain maximum flashover voltage during raining.
The rain sheds are made in such a way that they should not disturb the voltage distribution. They are so designed that their subsurface at a right angle to the electromagnetic lines of force.
Types of Pin Insulators:-
- Ceramic Pin Insulators
- Glass Pin Insulators
- Polymer Pin Insulators
- Porcelain Pin Insulators
Advantages and disadvantages of pin type insulator-
Advantages of Pin Insulator-
- High Mechanical Strength: Pin insulators can withstand heavy loads and mechanical stresses.
- Excellent Electrical Insulation: Pin insulators provide high insulation resistance, minimizing electrical losses.
- Durability: Pin insulators are resistant to environmental factors like weather, pollution, and chemicals.
- Low Maintenance: Pin insulators require minimal maintenance, reducing maintenance costs.
- Compact Design: Pin insulators have a compact design, making them ideal for space-constrained applications.
- High Voltage Withstand: Pin insulators can withstand high voltages, making them suitable for high voltage applications.
- Chemical Resistance: Pin insulators are resistant to chemical corrosion, ensuring long-term reliability.
- UV Resistance: Pin insulators can withstand ultraviolet (UV) radiation, reducing degradation.
- Wide Temperature Range: Pin insulators operate effectively in extreme temperatures.
- Cost-Effective: Pin insulators are cost-effective compared to other insulator types.
Disadvantages of Pin Insulator-
- Limited Voltage Rating: Pin insulators have lower voltage ratings compared to other insulator types.
- Fragility: Pin insulators can be brittle and prone to breakage.
- Weather-Related Issues: Exposure to extreme weather conditions can reduce pin insulator performance.
- Pollution-Related Issues: Pollution can accumulate on pin insulators, reducing insulation effectiveness.
- Age-Related Deterioration: Pin insulators can deteriorate over time, reducing insulation properties.
- Limited Flexibility: Pin insulators have limited flexibility, making them unsuitable for applications requiring flexibility.
- High Dielectric Losses: Pin insulators can experience high dielectric losses, reducing efficiency.
- Radio Influence Voltage (RIV): Pin insulators can generate RIV, interfering with communication systems.
- Limited Current-Carrying Capacity: Pin insulators have limited current-carrying capacity.
- Installation Challenges: Pin insulators require precise installation to ensure optimal performance.
Application of pin type insulator-
- Overhead Power Lines
- Substations
- Transmission Lines
- Distribution Lines
- Electrical Transformers
- Switchgear
- Electrical Panels
pin type insulator 11kv-
A pin type insulator is widely used in power distribution systems for lines operating at 11 kV. Typically made from porcelain, glass, or polymer materials, providing good electrical insulation and mechanical strength. The minimum creepage distance (the surface path along the insulator) for 11 kV systems is around 320 mm, which helps prevent leakage current during high humidity or pollution.
eight: Approximately 180-220 mm Diameter: Around 150 mm These dimensions can vary slightly depending on manufacturer and application.
Read also-
Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQ) on Pin Type Insulators with Answers-
- What is the main function of a pin type insulator?
a) To conduct electricity
b) To insulate conductors from the pole
c) To reduce the current
d) To increase the voltage Answer: b) To insulate conductors from the pole
- What is the typical maximum voltage rating for a single pin type insulator?
a) 11 kV
b) 33 kV
c) 66 kV
d) 132 kV Answer: b) 33 kV
- What material is commonly used to manufacture pin type insulators?
a) Aluminum
b) Copper
c) Porcelain
d) Lead Answer:c) Porcelain
- What happens when the surface of a pin insulator becomes contaminated?
a) It improves insulation
b) It reduces leakage current
c) It increases the chance of flashover
d) It increases the system voltage Answer: c) It increases the chance of flashover
- How is the conductor secured on the pin type insulator?
a) With screws
b) With bolts
c) With binding wire
d) With glue Answer: c) With binding wire
- Which part of the distribution system typically uses pin type insulators?
a) Substations
b) Low-voltage lines
c) High-voltage transmission lines
d) Medium-voltage distribution lines Answer: d) Medium-voltage distribution lines
- What is the main reason pin type insulators are not used for voltages above 33 kV?
a) Too expensive
b) Require complex installation
c) Become too large and heavy
d) Cannot withstand mechanical stress Answer: c) Become too large and heavy
- What is the minimum creepage distance required for a 11 kV pin insulator?
a) 220 mm
b) 320 mm
c) 100 mm
d) 450 mm Answer: b) 320 mm
- Which of the following is a disadvantage of pin type insulators?
a) Suitable for high-voltage lines
b) Easy to maintain
c) Brittle and prone to breakage
d) Works well in polluted areas Answer: c) Brittle and prone to breakage
- What is the primary mounting arrangement for a pin type insulator?
a) Suspended from a tower
b) Fixed to a cross-arm using a metal pin
c) Installed on the ground
d) Hung with a chain
Answer: b) Fixed to a cross-arm using a metal pin
- Which environmental factor is most likely to affect the performance of pin type insulators?
a) Rain and wind
b) Humidity and pollution
c) Snowfall
d) Underground moisture
Answer: b) Humidity and pollution
- What is the primary cause of failure in pin type insulators?
a) Overheating
b) Flashover due to contamination
c) Mechanical fatigue
d) Rusting of the pin
Answer: b) Flashover due to contamination
- Which of the following is a key advantage of pin type insulators?
a) Suitable for extremely high voltages
b) Cost-effective for low and medium voltage systems
c) Requires suspension chains
d) Works best with long spans
Answer: b) Cost-effective for low and medium voltage systems
- What shape is commonly used for the surface of pin insulators to reduce leakage?
a) Smooth cylinder
b) Ribbed or grooved
c) Flat plate
d) Hollow tube
Answer: b) Ribbed or grooved
- Which test is commonly performed to ensure the quality of a pin type insulator?
a) Voltage drop test
b) High voltage flashover test
c) Megger test
d) Surge current test
Answer: b) High voltage flashover test
- Which of the following insulator types is better suited for voltages above 33 kV?
a) Pin type insulator
b) Suspension insulator
c) Strain insulator
d) Shackle insulator
Answer: b) Suspension insulator
- What type of pin is typically used to mount pin type insulators?
a) Wooden pin
b) Iron or steel pin
c) Plastic pin
d) Copper pin
Answer: b) Iron or steel pin
- Why are multiple pin insulators used for higher voltage levels?
a) To distribute the mechanical load
b) To increase creepage distance
c) To reduce conductor size
d) To prevent electrical theft
Answer: b) To increase creepage distance
- What type of failure is associated with water penetration inside the insulator material?
a) Mechanical fracture
b) Insulation puncture
c) Conductor corrosion
d) Pin degradation
Answer: b) Insulation puncture
- What is the typical position of a pin type insulator on the pole?
a) Suspended from the bottom
b) Fixed horizontally on the cross-arm
c) Mounted on top of the cross-arm
d) Buried in the ground
Answer: c) Mounted on top of the cross-arm