Types of resistor MCQ is A resistor is a passive electrical component that limits or regulates the flow of electrical current in a circuit. It also divides voltage and can be used to generate heat or reduce signal levels.
Resistors obey Ohm’s Law, V=IR where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance. By introducing resistance, they control the current flow in a circuit.
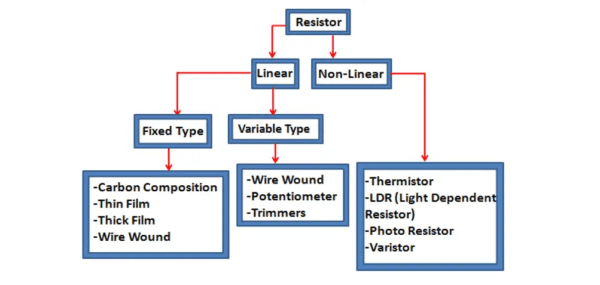
Fixed Resistors: Carbon film, metal film, wire-wound, etc.
Variable Resistors: Potentiometers, rheostats.
Special Resistors: Thermistors, photoresistors (LDRs), varistors.
NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient): Resistance decreases as temperature increases.
PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient): Resistance increases as temperature increases.
Thermistors are used in temperature sensing and protection circuits.
Carbon Film Resistor: Made of a thin carbon layer, suitable for low-power applications.
Wire-Wound Resistor: Made by winding a wire (usually nichrome) around a core, suitable for high-power applications.
| Colour | Colour code |
| Black | 0 |
| Brown | 1 |
| Red | 2 |
| Orange | 3 |
| Yellow | 4 |
| Green | 5 |
| Blue | 6 |
| Violet | 7 |
| Grey | 8 |
| White | 9 |
What is Tolerance in Resistors?
Following is a table with tolerance of resistor:
| Colour | Tolerance |
| Brown | ±1% |
| Red | ±2% |
| Gold | ±5% |
| Silver | ±10% |
Types of resistor MCQ-
Q. What type of resistor changes its resistance based on temperature?
A) Potentiometer
B) Thermistor
C) Varistor
D) Photoresistor
- Answer: B) Thermistor
- Explanation: A thermistor is a temperature-sensitive resistor. NTC thermistors decrease resistance with temperature, while PTC thermistors increase resistance.
Q. What does the fourth band on a resistor’s color code represent?
A) Resistance value
B) Multiplier
C) Tolerance
D) Power rating
- Answer: C) Tolerance
- Explanation: The fourth band indicates the tolerance, which specifies the possible deviation from the resistor’s nominal value.
Q. Which resistor is best suited for high-power applications?
A) Carbon film resistor
B) Wire-wound resistor
C) Metal film resistor
D) Variable resistor
- Answer: B) Wire-wound resistor
- Explanation: Wire-wound resistors can handle high power due to their construction using wire wound around a core.
Q. A resistor has color bands: Red, Violet, Yellow, and Gold. What is its resistance?
A) 270 kΩ ± 5%
B) 270 Ω ± 5%
C) 27 kΩ ± 10%
D) 2700 Ω ± 5%
- Answer: A) 270 kΩ ± 5%
- Explanation:
- Red = 2, Violet = 7 (first two digits).
- Yellow = 10410^4104 (multiplier).
- Gold = ±5% (tolerance).
Resistance = 27×104=270,000 Ω=270 kΩ27 \times 10^4 = 270,000 \, \Omega = 270 \, k\Omega27×104=270,000Ω=270kΩ.
Q. Which of the following is a variable resistor?
A) Thermistor
B) Photoresistor
C) Potentiometer
D) Metal oxide resistor
- Answer: C) Potentiometer
- Explanation: A potentiometer is a variable resistor used to adjust resistance in a circuit.
Q. Which resistor changes its resistance based on light intensity?
A) Thermistor
B) Photoresistor
C) Potentiometer
D) Varistor
- Answer: B) Photoresistor
- Explanation: A photoresistor (or Light Dependent Resistor, LDR) decreases its resistance as light intensity increases, making it useful in light-sensing applications.
Q. What happens to the current if the resistance in a circuit increases, assuming constant voltage?
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Remains constant
D) Doubles
- Answer: B) Decreases
- Explanation: According to Ohm’s Law (I=VRI = \frac{V}{R}I=RV), if RRR increases and VVV is constant, the current III decreases.
Q. Which resistor is designed to protect circuits from voltage surges?
A) Thermistor
B) Varistor
C) Potentiometer
D) Carbon film resistor
- Answer: B) Varistor
- Explanation: A varistor changes its resistance based on voltage. It protects circuits by clamping high voltages and preventing surges.
Q. What is the tolerance of a resistor with a silver band as the fourth color?
A) ±1%
B) ±2%
C) ±5%
D) ±10%
- Answer: D) ±10%
- Explanation: The silver band in the fourth position indicates a tolerance of ±10%, meaning the actual resistance may vary by this percentage from the nominal value.
Q. Which type of resistor is commonly used for precision applications?
A) Carbon composition resistor
B) Metal film resistor
C) Wire-wound resistor
D) Thermistor
- Answer: B) Metal film resistor
- Explanation: Metal film resistors offer high precision and stability, making them ideal for applications requiring accurate resistance values.
Q. What is the main disadvantage of a carbon composition resistor?
A) High cost
B) Poor tolerance and stability
C) Large size
D) Low power handling
- Answer: B) Poor tolerance and stability
- Explanation: Carbon composition resistors are inexpensive but have poor tolerance and stability compared to other types like metal film or wire-wound resistors.
Q. Which resistor type is best for handling very high temperatures?
A) Carbon film resistor
B) Metal oxide resistor
C) Wire-wound resistor
D) Photoresistor
- Answer: B) Metal oxide resistor
- Explanation: Metal oxide resistors are designed to withstand high temperatures and are more stable than carbon film resistors in such conditions.
Q. Which of the following resistors is non-linear?
A) Carbon film resistor
B) Wire-wound resistor
C) Thermistor
D) Metal oxide resistor
- Answer: C) Thermistor
- Explanation: Thermistors are non-linear because their resistance changes with temperature in a non-linear manner, unlike other resistors that have a constant resistance.
Q. What is the purpose of a fuse resistor?
A) To provide variable resistance
B) To limit current under normal conditions and act as a fuse during overcurrent
C) To protect against voltage surges
D) To act as a temperature sensor
- Answer: B) To limit current under normal conditions and act as a fuse during overcurrent
- Explanation: A fuse resistor combines the functionality of a resistor and a fuse, protecting circuits by breaking the connection when current exceeds a safe limit.
Q. What does a potentiometer adjust in a circuit?
A) Voltage
B) Current
C) Resistance
D) All of the above
- Answer: D) All of the above
- Explanation: A potentiometer is a variable resistor that can adjust voltage, current, and resistance depending on its configuration in the circuit.
Q. In a circuit, if the voltage is doubled and the resistance remains constant, what happens to the current?
A) Halves
B) Doubles
C) Remains the same
D) Increases fourfold
- Answer: B) Doubles
- Explanation: According to Ohm’s Law (I=VRI = \frac{V}{R}I=RV), if VVV is doubled and RRR is constant, the current III also doubles.
Q. Which resistor is commonly used for voltage division in circuits?
A) Photoresistor
B) Potentiometer
C) Thermistor
D) Carbon composition resistor
- Answer: B) Potentiometer
- Explanation: Potentiometers are used in voltage dividers because they allow for adjustable voltage output by varying the resistance between two points.
Q. What is the significance of the power rating of a resistor?
A) It determines the voltage the resistor can handle.
B) It indicates the maximum current the resistor can allow.
C) It specifies the maximum heat the resistor can dissipate without damage.
D) It shows the tolerance of the resistor.
- Answer: C) It specifies the maximum heat the resistor can dissipate without damage.
- Explanation: The power rating indicates the resistor’s ability to dissipate heat safely, calculated using P=I2RP = I^2RP=I2R.
Q. Which of the following factors affects the resistance of a conductor?
A) Material
B) Length
C) Cross-sectional area
D) All of the above
- Answer: D) All of the above
- Explanation: Resistance depends on the material’s resistivity, the length of the conductor (directly proportional), and the cross-sectional area (inversely proportional).
Q. What is the primary use of a metal oxide resistor?
A) High-temperature applications
B) Precision circuits
C) Low-power circuits
D) Light-sensing applications
- Answer: A) High-temperature applications
- Explanation: Metal oxide resistors are designed to operate reliably in high-temperature environments due to their robust construction.