A suspension type insulator is a type of electrical insulator used in high-voltage transmission and distribution systems. It is designed to suspend the overhead conductor or power line and electrically isolate it from the supporting structures, such as towers or poles. This ensures that electrical energy is transmitted safely without leaking to the ground or causing dangerous short circuits.
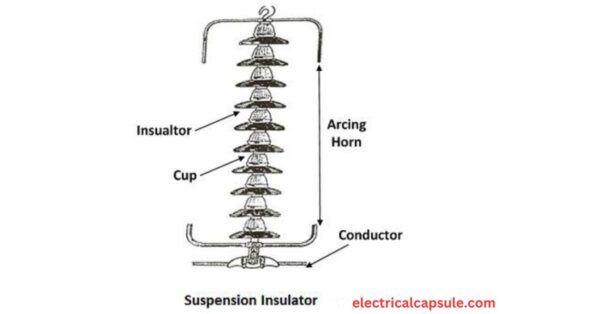
In higher voltage, beyond 33KV, it becomes uneconomical to use pin insulator because size, weight of the insulator become more. Handling and replacing bigger size single unit insulator are quite difficult task. For overcoming these difficulties, suspension insulator was developed.
types of suspension insulators–
They are further classified into two types, they are.
- Cap and Pin Type
- Hewlett or Interlink Type
1-Cap and Pin Type-
The cap and pin type suspension insulator is the most widely used design in high-voltage power transmission lines. It consists of individual disc-shaped units made of porcelain or glass, which are connected in series by metallic caps and pins. Each disc can withstand a specific voltage level, and adding more discs to the string increases the overall voltage capacity.
2-Hewlett or Interlink Type Suspension Insulator–
The Hewlett or interlink type suspension insulator is a specialized design for high-voltage overhead transmission lines. This type consists of two curved metal channels arranged perpendicularly 90 degrees to each other, with a U-shaped steel link connecting the units. This design provides additional mechanical strength, ensuring that even if the porcelain elements fracture, the metallic link continues to support the conductor, minimizing the risk of power disruptions.
Compared to cap-and-pin types, interlink or Hewlett designs offer superior mechanical reliability. However, their porcelain components may be more vulnerable to high electrical stress, resulting in a relatively lower puncture resistance. The interlink insulator’s robust mechanical configuration makes it especially suitable for scenarios where stability and continuity are critical, such as in challenging environmental conditions or on long-span transmission lines.
This type of insulator helps maintain the electrical isolation between lines and also supports the conductor’s weight by hanging vertically from the tower structure, ensuring consistent performance under varying load and weather conditions.
Read also-
Advantages of Suspension Type Insulator-
- Each suspension disc is designed for normal voltage rating 11KV (Higher voltage rating 15KV), so by using different numbers of discs, a suspension string can be made suitable for any voltage level.
- If any one of the disc insulators in a suspension string is damaged, it can be replaced much easily.
- Mechanical stresses on the suspension insulator is less since the line hanged one flexible suspension string.
- As the current carrying conductors are suspended from supporting structure by suspension string, the height of the conductor position is always less than the total height of the supporting structure. Therefore, the conductors may be safe from lightening.
disadvantages of Suspension Type Insulator–
- Suspension insulator string costlier than pin and post type insulator.
- Suspension string requires more height of supporting structure than that for pin or post insulator to maintain same ground clearance of current conductor.
- The amplitude of free swing of conductors is larger in suspension insulator system, hence, more spacing between conductors should be provided.
Application of suspension type insulator–
- High-Voltage Transmission Lines
- Distribution Lines
- Switchyards and Substations
- Railway Electrification Systems
- Flexible Line Design
- Polluted or Coastal Areas
- High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Systems
- Wind Farms
- Solar Power Plants
- Long-Distance Power Transmission
Exam point Suspension Insulator–
1-This type of insulator is not economical below 33kv.
2- It consist of a number of porcelain discs connected in series by metal links in the form of a string.
3-The conductor is suspended at the bottom end of the string while the other end of the strings is screwed to the cross-arm of the tower.
4- For a working voltage of 66kv, six discs in series will be provided on the insulator string.
Difference Between Pin Insulator and Suspension Type Insulator-
| Parameter | Pin Insulator | Suspension Insulator |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Single unit mounted on a cross-arm or pole. | Made of multiple disc units connected in a string. |
| Voltage Handling | Suitable for lower voltage levels (up to 33 kV). | Used for high-voltage transmission lines (above 33 kV). |
| Installation Position | Installed horizontally on cross-arms. | Hangs vertically from towers or poles. |
| Modularity | Not modular; one piece only. | Modular; more discs can be added to increase voltage capacity. |
| Mechanical Strength | Limited mechanical load capacity. | Can bear higher mechanical loads, ideal for long spans. |
| Failure Handling | If the insulator breaks, it fails entirely. | If one disc breaks, the rest of the string can still function. |
| Maintenance | Less prone to pollution-related issues. | Requires periodic cleaning in polluted areas to avoid flashover. |
| Typical Applications | Used in distribution networks and transformers. | Used in transmission lines and high-voltage networks. |
| Cost | Cheaper for low-voltage networks. | More expensive due to modular design and higher reliability. |
| Common Materials | Porcelain or polymer. | Porcelain, glass, or polymer. |
Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQ) on suspension type insulator with Answers-
1. What is the primary function of a suspension insulator?
A. To support the mechanical load of the conductor
B. To provide electrical insulation between the conductor and the tower
C. To convert AC to DC
D. To step down voltage levels
Answer: B
Explanation: Suspension insulators electrically isolate the conductor from the supporting structures, preventing current leakage to the ground.
2. Which material is most commonly used for making suspension insulators?
A. Copper
B. Porcelain
C. Rubber
D. Steel
Answer: B
Explanation: Suspension insulators are typically made from porcelain, glass, or polymer materials because of their excellent insulating properties.
3. How does increasing the number of discs in a suspension insulator string affect it?
A. Decreases the overall mechanical strength
B. Increases the current-carrying capacity
C. Increases the voltage rating of the string
D. Reduces power loss
Answer: C
Explanation: Adding more discs increases the total insulation level, making the string suitable for higher voltage applications.
4. Which of the following is a disadvantage of the cap and pin type suspension insulator?
A. Easy maintenance
B. Uneven voltage distribution across discs
C. Modular structure
D. High mechanical strength
Answer: B
Explanation: In cap-and-pin insulators, the disc closest to the conductor experiences the most electrical stress, leading to uneven voltage distribution.
5. In which environment are polymer suspension insulators preferred?
A. Coastal regions with high humidity
B. Hot deserts with minimal pollution
C. Underground transmission lines
D. Urban areas with low pollution levels
Answer: A
Explanation: Polymer insulators are preferred in highly polluted or coastal regions due to their hydrophobic properties, which reduce contamination and flashovers.
6. What type of mechanical stress do suspension insulators primarily endure?
A. Compression
B. Torsion
C. Tension
D. Shear
Answer: C
Explanation: Suspension insulators are subjected to tensile stress because they hang vertically, supporting the conductor’s weight.
7. What is the typical failure mode of a glass suspension insulator?
A. Thermal expansion
B. Shattering under stress
C. Rusting of metal parts
D. Short-circuit due to moisture
Answer: B
Explanation: Glass insulators can shatter under mechanical stress, but they do not corrode, and their broken parts often remain in place, preventing line failure.
8. What is the advantage of using interlink (Hewlett) type suspension insulators?
A. Reduces electrical losses
B. Increases the tensile strength of the string
C. Ensures mechanical continuity even after a disc failure
D. Reduces corona discharge
Answer: C
Explanation: In Hewlett or interlink types, even if one disc fails, the mechanical connection remains intact through the interlink.
9. What is the primary advantage of using suspension insulators over pin-type insulators?
A. Lower cost for lower voltage levels
B. Can be used for higher voltage applications
C. Easier to install on wooden poles
D. Offers better heat dissipation
Answer: B
Explanation: Suspension insulators are preferred for higher voltage lines because they provide scalable insulation. By increasing the number of discs, they can handle extremely high voltages, unlike pin-type insulators, which are limited to lower voltage levels.
10. How are the discs in a suspension insulator string connected?
A. Through insulating resin layers
B. Using metal rods and bolts
C. With metal caps and pins
D. By adhesive bonding
Answer: C
Explanation: Each disc in a suspension insulator string is connected by metal caps and pins, providing mechanical strength and electrical insulation.
11. Which phenomenon is reduced by using suspension insulators in long spans?
A. Skin effect
B. Corona discharge
C. Voltage drops
D. Magnetic interference
Answer: B
Explanation: Suspension insulators help reduce corona discharge because their disc design minimizes sharp edges, which would otherwise enhance ionization around conductors at high voltages.
12. What type of loading is a suspension insulator system designed to handle?
A. Vertical loading only
B. Both horizontal and vertical loading
C. Axial torsion
D. Bending loads exclusively
Answer: B
Explanation: Suspension insulators manage both vertical (from the conductor’s weight) and horizontal loads (due to wind and line tension) effectively.
13. Why are glass suspension insulators often preferred over porcelain?
A. Glass is cheaper to manufacture
B. Glass has higher resistance to UV degradation
C. Faulty glass insulators shatter visibly, aiding quick detection
D. Glass is lighter than porcelain
Answer: C
Explanation: When glass insulators fail, they shatter visibly, making it easier for maintenance crews to identify faulty units compared to porcelain, which can crack without external signs
14.What is the typical voltage rating for suspension type insulator
A) Low voltage (less than 1 kV)
B) Medium voltage (1-33 kV)
C) High voltage (33-132 kV)
D) Extra high voltage (above 132 kV)
Answer: D) Extra high voltage (above 132 kV)
15.What is the primary disadvantage of suspension type insulators?
A) Limited voltage rating
B) Fragility
C) High maintenance
D) Limited flexibility
Answer: D) Limited flexibility
16.What is the purpose of the hardware in a suspension type insulator?
A) Electrical connection
B) Mechanical support
C) Insulation enhancement
D) Weight reduction
Answer: B) Mechanical support
17.Which type of insulator is suitable for high-voltage direct current (HVDC) applications?
A) Suspension type insulator
B) Line post insulator
C) Station post insulator
D) Pin-type insulator
Answer: A) Suspension type insulator